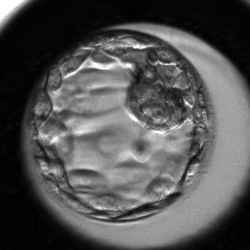
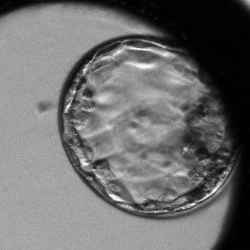
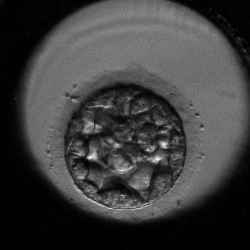
Day‑Five Embryos Grading System

Senior embryologists behind the CATI tool developed a smart day‑five embryos grading system which defines rules based on the timing of morphokinetic markers. Grading means sorting the embryos in correlation with their implantation potential (IP). The IP of embryos in our grading system is suggested based on the assumption that the embryos are ideally transferred into an ideal in-vivo environment.
| Grade Part | Description | ||
|---|---|---|---|
|
1
A
A
The 1st number |
Stage of Development The Number in the first position of the CATI grading system represents a degree of embryo's blastocyst cavity and its progress in hatching out of the zona pellucida on the scale from 1 to 8. 1
A
A
Hatching Blastocyst
2
A
A
Expanded Blastocyst
3
A
A
Expanding Blastocyst
4
A
A
Blastocyst
5
A
A
Early Blastocyst
6
A
A
Morula
7
D
8
8
|
||
|
1
A
A
The 2nd letter |
Quality of Cleavage Second position in the grading system represents the quality of an embryo. Values (A, B, C, D) are assigned according to observations of cell division occurring within the embryo. 1
A
A
A is normal development with linear expansion
1
B
A
B is development with collapse
1
C
A
C means low number of trophectoderm cells
1
D
A
D means degenerated
|
||
|
1
A
A
The 3rd letter |
Event Timing The 3rd refers to timing and count of events — expansion, collapse — that are typical for the stage of development and the quality of cleavage. For normal development (A): 1‑5
A
A
delayed or early onset of expansion
1‑5
A
B
middle onset of expansion
1‑5
A
C
late onset of expansion
6
A
A
delayed compaction of blastomeres
For development with collapse (B): 1‑4
B
A
one early collapse
1‑4
B
B
one late collapse
1‑4
B
C
multiple collapses
For low number of trophectoderm cells (C): 1‑6
C
A
low count of trophectoderm cells
For degenerated (D): 1‑8
D
A
degenerated (no significant event observed)
|
||
|
1
C
A
Low
|
The Likelihood of Successful Implantation An expression of the embryo's capability to achieve successful implantation. The values are:
|
||
List of Grades
You are already familiar with the grading system's basics. Below, you will find all defined grades together with time‑lapse embryos examples and morphokinetic rules.
Hatching Blastocyst
Hatching blastocyst with early onset of expansion
Hatching blastocyst starting expansion within 100 hrs after fertilization.
Expansion is linear without any collapse/re-expansions.
Hatching blastocyst with middle onset of expansion
Hatching blastocyst starting expansion after 100 hrs from fertilization.
Expansion is linear without any collapse/re-expansions.
Hatching blastocyst with early collapse
Hatching blastocyst starting expansion within 100 hrs after fertilization.
Expansion is interrupted by one collapse of blastocoel occurring within 105 hrs after fertilization.
Hatching blastocyst with late collapse
Hatching blastocyst starting expansion after 100 hrs after fertilization.
Expansion is interrupted by one collapse of blastocoel occurring after 105 hrs after fertilization.
Hatching blastocyst with multiple collapses
Hatching blastocyst starting expansion within 110 hrs after fertilization.
Expansion is interrupted by multiple collapses of blastocoel.
Hatching blastocyst with low number of trophectoderm cells
This embryo has few TE cells, forming a loose epithelium and in extreme situation TE is formed by very few large cells.
Many of the abnormally cleaved cells are excluded from the embryo into the PVS (periviteline space) and are squeezed under the ZP by growing blastocyst.
One or more collapses of blastocoel can be detected.
Hatching blastocyst with degeneration/vacuolization of majority of the cells
Hatching blastocyst with total collapse of blastocoel cavity without re-expansion.
The blastomeres undergo degeneration that is expressed by the total cell lysis or extreme vacuolization.
No further progress in development is achieved.
One or more collapses of blastocoel can be detected before total collapse.
Expanded Blastocyst
Expanded blastocyst with early onset of expansion
Expanded blastocyst starting expansion within 100 hrs after fertilization.
Expansion is linear without any collapse/re-expansions.
Expanded blastocyst with middle onset of expansion
Expanded blastocyst starting expansion from 100–105 hrs after fertilization.
Expansion is linear without any collapse/re-expansions.
Expanded blastocyst with late onset of expansion
Expanded blastocyst starting expansion after 105 hrs after fertilization.
Expansion is linear without any collapse/re-expansions.
Expanded blastocyst with early collapse
Expanded blastocyst starting expansion within 100 hrs after fertilization.
Expansion is interrupted by one collapse of blastocoel occurring 100–105 hrs after fertilization.
Expanded blastocyst with late collapse
Expanded blastocyst starting expansion within 105 hrs after fertilization.
Expansion is interrupted by one collapse of blastocoel occurring 105–110 hrs after fertilization.
Expanded blastocyst with multiple collapses
Expanded blastocyst starting expansion within 105 hrs after fertilization.
Expansion is interrupted by 2 and more collapses of blastocoel.
Expanded blastocyst with low number of trophectoderm cells
This embryo has few TE cells, forming a loose epithelium and in extreme situations, TE is formed by very few large cells.
Many of the abnormally cleaved cells are excluded from the embryo into the PVS (peri viteline space) and are squeezed under the ZP by growing blastocyst.
Expansion is interrupted by one or more collapses of blastocoel.
Expanded blastocyst with degeneration/vacuolization of majority of the cells
Expanded blastocyst with total collapse of blastocoel cavity without re-expansion.
The blastomeres undergo degeneration that is expressed by the total cell lysis or extreme vacuolization.
No further progress in development is achieved.
One or more collapses of blastocoel can be detected before total collapse.
Expanding Blastocyst
Expanding blastocyst
Expanding blastocyst starting expansion within 105 hrs after fertilization.
The volume of the blastoceol cavity increased the diameter of the embryo and thinned the zona pellucida.
Expansion is linear without any collapse/re-expansions.
Expanding blastocyst with one or more collapses
Expanding blastocyst starting expansion after 105 hrs after fertilization.
The volume of the blastoceol cavity increased the diameter of the embryo and thinned the zona pellucida.
Expansion is interrupted by one or more collapses of blastocoel.
Expanding blastocyst with low number of trophectoderm cells
This embryo has few TE cells, forming a loose epithelium and in extreme situation TE is formed by very few large cells.
Many of the abnormally cleaved cells are excluded from the embryo into the PVS (peri viteline space) and are squeezed under the ZP by growing blastocyst.
Expansion is interrupted by one or more collapses of blastocoel.
Expanding blastocyst with degeneration/vacuolization of the majority of cells
Expanding blastocyst with total collapse of blastocoel cavity without re-expansion.
The blastomeres undergo degeneration that is expressed by the total cell lysis or extreme vacuolization.
No further progress in development is achieved.
One or more collapses of blastocoel can be detected before total collapse.
Blastocyst
Blastocyst
Blastocyst starting expansion after 105 hrs after fertilization.
Blastocoel cavity completely fills the embryo.
No periviteline space is visible.
The blastocyst volume still did not increase the diameter of the embryo to the extendt needed to thin the zona pellucida.
Expansion is linear without any collapse/re-expansions.
Blastocyst with one or more collapses
Blastocyst starting expansion after 105 hrs after fertilization.
Blastocoel cavity completely fills the embryo.
No periviteline space is visible.
The blastocyst volume still did not increase the diameter of the embryo to the extent needed to thin the zona pellucida.
Expansion is interrupted by one or more collapses of blastocoel.
Blastocyst with low number of trophectoderm cells
TE is formed by very few large cells.
Many of the abnormally cleaved cells are excluded from the embryo into the PVS (peri viteline space) and are squeezed under the ZP by growing blastocyst.
One or more collapses of blastocoel can be detected.
Blastocyst with degeneration/vacuolization of the majority of cells
Blastocyst with total collapse of blastocoel cavity without re-expansion.
The blastomeres undergo degeneration that is expressed by the total cell lysis or extreme vacuolization.
No further progress in development is achieved.
One or more collapses of blastocoel can be detected before total collapse.
Early Blastocyst
Early blastocyst
Early blastocyst with visible blastocoel cavity formation.
The cavity fills less than half volume of the embryo.
Perivitelline space (PVS) is still present and no degenerated cells are found in the PVS.
Early blastocyst with low number of cells
Early blastocyst with visible blastocoel cavity having low number of cells.
Many of the abnormally cleaved cells are excluded from the embryo into the PVS (periviteline space).
Expansion is interrupted by one or more collapses of blastocoel.
Early blastocyst with degeneration/vacuolization of the majority of cells
Early blastocyst with total collapse of blastocoel cavity without re-expansion.
The blastomeres undergo degeneration that is expressed by the total cell lysis or extreme vacuolization.
No further progress in development is achieved.
One or more collapses of blastocoel can be detected before total collapse.
Morula
Morula
No blastocoel cavity is visible.
No degenerated cells are found in the PVS (perivitelline space).
Morula with low number of cells
No cavity is visible.
Embryo is formed by very few large cells (up to 8).
Some lysed and/or vacuolized blastomeres are excluded from the embryo into the PVS (peri viteline space).
Morula with degeneration/vacuolization of majority of the cells
Blastomeres undergo degeneration.
Degeneration is expressed by a total cell lysis or extreme vacuolization.
No further progress in development is achieved.
Arrested Embryo
Arrested/Degenerated
The embryos are arrested in their development.
There is no progress in cell cleavages.
Cells frequently undergo degeneration and vacuolization/lysis.
The development can stop at any time (from 2cc stage to more than 8–16cc).
No signs of the cell compaction are visible.
Unfertilized
Unfertilized/Uncleaved
No signs of pronuclei formation.
In some cases PN are present but no cleavage occurs.
The oocytes can be lysed soon after ICSI or can undergo degeneration during prolonged culture.
In case of extreme vacuole formation, the oocyte can increase its diameter and that is followed by the total lysis of the cell.
Implantation Chance by Grades
The implantation potential (IP) is an expression of the embryo's capability to achieve successful implantation. Because implantation is a multifactorial event, IP of embryos in our grading system is suggested based on the assumption that the embryos are ideally transferred into an ideal in-vivo environment.